Step into the wild, wild web where cyber threats lurk around every corner and your personal data is more sought after than a hidden treasure! But fear not, brave internet explorer (pun intended), for we have the ultimate weapon in our arsenal – Virtual Private Networks, the caped crusaders of online security and digital freedom! In this all-in-one guide, we’ll go over what a Virtual Private Network is, reveal the well hidden secrets of VPNs, arm you with the knowledge to make savvy decisions, and expose the truth behind their flashy promises. Let the quest begin!
- Please Read this before you dive in:
🚨Disclaimer: The following article may mention various VPNs for informational purposes only. Please note that ShieldMe, including its affiliates and writers, does not have any direct affiliation or partnership with the mentioned VPNs. Additionally, ShieldMe does not officially recommend or endorse any specific VPN service mentioned in this article. ShieldMe gives credit to the mentioned VPN services solely as a courtesy and not as an affiliation. The information provided is based on general research and has been included to explain the context in a clear way. Users are encouraged to conduct their own thorough evaluation and assessment of any VPN service before making a decision. ShieldMe shall not be held responsible for any actions, outcomes, or consequences resulting from the use of any VPN service mentioned in this article. Users are advised to exercise caution and discretion when selecting and utilizing a VPN service and should refer to the respective VPN provider's terms of service, privacy policy, and applicable laws and regulations.
1) Introduction: What exactly is a VPN?

A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a widely used technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection between your device and the internet. It acts as a protective shield, safeguarding your online activities, data, and identity from prying eyes and potential threats. When you connect to a VPN server, your internet traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel, making it way harder for anyone to intercept or decipher your sensitive information.
2) How VPNs Work: Decoding the Technology Behind Online Anonymity

Virtual Private Networks are a way of extending the end of your network to exit somewhere else in the world.
When you initiate a connection with a VPN server, your device (such as a computer, smartphone, or tablet) establishes a secure tunnel through which your data is encrypted before being transmitted over the internet. This encryption process converts your data into an unreadable format, ensuring that even if intercepted, it remains indecipherable to unauthorized individuals.
To achieve this magic, VPNs use fancy encryption techniques with names like OpenVPN, IPSec, or WireGuard. These are the “secret codes” that scramble your data and make it super hard for anyone to crack. It's like speaking in a secret language that only you and the VPN server understand.
VPNs also do this cool thing called tunneling. They wrap your encrypted data inside another package like a grilled cheese sandwich, creating a virtual tunnel for it to travel through. This clever trick makes it look like your internet traffic is coming from the VPN server's location, not yours. So, it's like you're surfing the web undercover, keeping your real IP address hidden.
After initializing a connection and sending your data through the tunnel, the destination server receives the packet and recognizes it as an encrypted packet. It decrypts the packet using the appropriate encryption key, revealing the original data.
Once the data packet is decrypted, the destination server processes the contents according to the specific application or service it provides. For example, if the destination server is a web server, it will process the packet as an HTTP request and respond accordingly.
After processing the packet, the destination server sends a response back to the VPN server. The response follows a similar route as the original packet but in the reverse direction.
When the VPN server receives the response from the destination server, it encrypts the response packet to maintain privacy and security.
The encrypted response packet is sent back to your device through the same VPN connection. The VPN client on your device receives the packet, decrypts it, and presents the response to your application or browser.
This process ensures your data is encrypted in transit and shifts the trust form your ISP to the VPN company.
3) The Benefits of VPNs: Unlocking a Secure and Free Internet Experience

-A VPN serves three main purposes:
a) It conceals your IP address from websites and your Internet Service Provider (ISP), shifting the trust from your ISP to the VPN service itself:
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) have the ability to log and track your internet activity. This includes the websites you visit, and even the specific content you access. This data can be valuable to ISPs and other third parties for various purposes, such as targeted advertising or market research. By logging and analyzing your internet activity, they can create user profiles and sell this information to advertisers or other companies.
To prevent ISPs from tracking and selling your internet activity, many people turn to Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a remote server before reaching its destination. This way, your ISP only sees encrypted data and cannot decipher the content of your online activities.

Credit: TunnelBear VPN However, it's crucial to choose a reputable VPN provider because, by using a VPN, you shift your trust from your ISP to the VPN provider. A good VPN provider will have strict no-logs policies, meaning they don't store any records of your online activities. They also employ strong encryption protocols and robust security measures. By selecting a trustworthy VPN, you can ensure that your internet activity remains private and secure.
b) It enables you to bypass some geographical restrictions or some content filters, granting you access to blocked content that would otherwise be unavailable for you:
Geoblocking is a technique used by content providers to restrict access to certain content based on the user's geographic location. For example, streaming platforms may limit their content library to specific regions due to licensing agreements or regulatory requirements. This can be frustrating when you encounter a message stating that the content is not available in your country.

Credit: Windscribe VPN A VPN can help bypass these geoblocks by allowing you to connect to a server located in a different country. When you connect to a VPN server in a non-restricted location, your internet traffic appears to originate from that server's location. As a result, you can access the content that would otherwise be blocked in your actual location.
However, it's worth noting that companies have become aware of VPN usage for bypassing geoblocks, and some have started blacklisting and blocking VPN connections. These companies actively identify and block IP addresses associated with popular VPN servers. To avoid disappointment, it's essential to check whether a particular VPN service is capable of bypassing the geoblocks imposed by the content provider you wish to access.
c) It encrypts your data, safeguarding against rare cyber threats such as Man-in-the-Middle attacks:
Most websites nowadays use the HTTPS protocol, which encrypts the data exchanged between your browser and the website. You can identify a secure connection by looking for a padlock icon in your browser "https://" in the URL. This encryption ensures that the data sent between you and the website is protected from eavesdropping and manipulation.
While HTTPS provides a high level of security, there are still instances where websites may use the insecure and outdated HTTP protocol. This is especially (and unfortunately) true for certain government or healthcare websites that have been slower to adopt HTTPS. When accessing websites over HTTP, your data is transmitted in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception and attacks.
By using a VPN, even when accessing HTTP websites, your data is encrypted and protected from potential attackers on the network. A VPN creates a secure tunnel between your device and the VPN server, preventing anyone from snooping on your internet traffic. This added layer of encryption ensures that your data remains secure, even on websites that don't use HTTPS.
It's important to note that while a VPN can enhance security for HTTP connections, it cannot protect against other security risks, such as malware or phishing attacks. Therefore, it's always recommended to exercise caution and use additional security measures like antivirus software and being mindful of the websites you visit and the files you download.
4) What VPNs Are Not: Debunking False Promises and Exposing Marketing Tactics

Now that we're well-versed in what a VPN can do, it's time to shed some light on what it cannot do. Here are some of the common marketing tricks VPN companies use to advertise their products:
“Military-Grade Encryption”: VPNs often boast about providing "military-grade encryption" to secure your data. While the term "military-grade encryption" sounds impressive, it simply refers to the same encryption algorithms and protocols used by many other companies and industries. It's a way of over-emphasizing that the encryption is strong and reliable, and to trick the user into thinking they are buying an impenetrable Death Star, while in reality it’s a clever marketing trick with a vulnerable exhaust port.

“Millitary-grade encryption” marketing trick - Credit: Hotspot Shield VPN “Magically increase your internet speed”: while some VPN providers offer ad and tracker blockers like Proton’s NetShield or Windscribe’s R.O.B.E.R.T, which might slightly improve load times in some websites, a VPN cannot enhance your internet speed since it relies on your existing internet bandwidth, effectively limiting its speed to your own internet connection.
Showcasing an anti-tracker feature (not deceptive marketing) - Credit: IVPN “Superman Syndrome”: VPNs are often marketed as tools for “Ultimate Anonymity and Invisibility”. While they can help mask your IP address and encrypt your internet traffic, they don't make you completely anonymous or invisible:

“One-click” for a safer internet marketing trick - Credit: ExpressVPN If you login with personal accounts or provide identifiable information, your actions will be tied back to you, for example logging in with your Instagram account while using a VPN won’t improve your anonymity at all.
VPN providers can still see your activities, and they may keep logs of your connection data. It's crucial to choose a reputable VPN service that has a strict no-logs policy. Keep in mind as well that your ISP can still see that you’re using a VPN.
“Malware protection tool”: While VPNs provide an additional layer of security by encrypting your data, they are not a one-stop solution for all security issues. They primarily protect your data while it's in transit between your device and the VPN server. If your device is compromised by malware or you visit insecure websites, a VPN alone cannot guarantee protection against these threats. It's important to maintain up-to-date security practices and use other security tools alongside a VPN.

Misleading guarantees - Credit: StrongVPN
5) Choosing the Right VPN Provider: Key Factors to Consider for a privacy-friendly VPN

Selecting an appropriate VPN can be an overwhelming task due to the abundance of options available in the market. While it might be hard to find a VPN that encompasses all of these attributes, it's advisable to seek a provider that incorporates as many of these factors as possible. Here are (in no particular order) 20 aspects to consider when choosing a VPN:
Strong Encryption Protocols: Look for a VPN provider that offers robust encryption protocols like OpenVPN, IPSec, or WireGuard. These protocols ensure that your data is securely encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.

Credit: Air VPN No-Logs Policy: A strict no-logs policy is crucial for privacy. It means that the VPN provider doesn't store any records of your online activities, ensuring that your browsing history, IP addresses, and connection timestamps are not logged.

Credit: Proton VPN Jurisdiction and Data Protection Laws: Consider the jurisdiction in which the VPN provider is based. Opt for providers located in countries with strong privacy laws and no mandatory data retention laws. This helps protect your data from being accessed or disclosed to third parties.

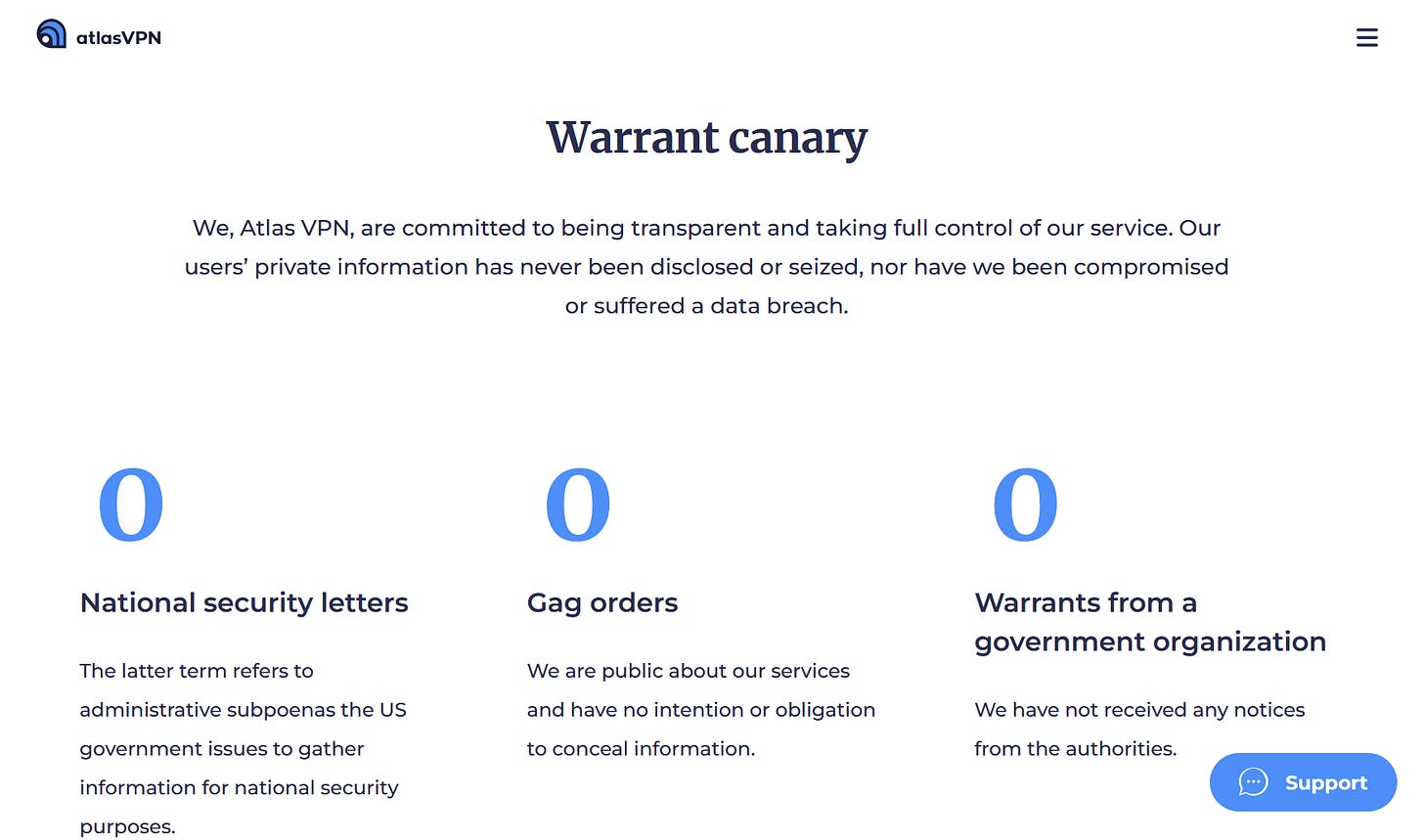
Credit: Proton VPN Warrant Canary: A warrant canary is a statement periodically published by a VPN provider, indicating that they have not received any secret government subpoenas or warrants. It serves as an indicator of transparency and protection against potential surveillance.
Credit: Atlas VPN DNS Leak Protection: DNS leaks can expose your online activities to your ISP or other entities. Ensure that the VPN provider has DNS leak protection mechanisms in place to prevent such leaks and ensure that all DNS requests are routed through the VPN.
Credit: PIA VPN Kill Switch: A kill switch (or kill switch-like feature) is an important feature that ensures your internet connection is immediately severed if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly. This prevents your traffic from being exposed to your ISP or other potential snoopers.
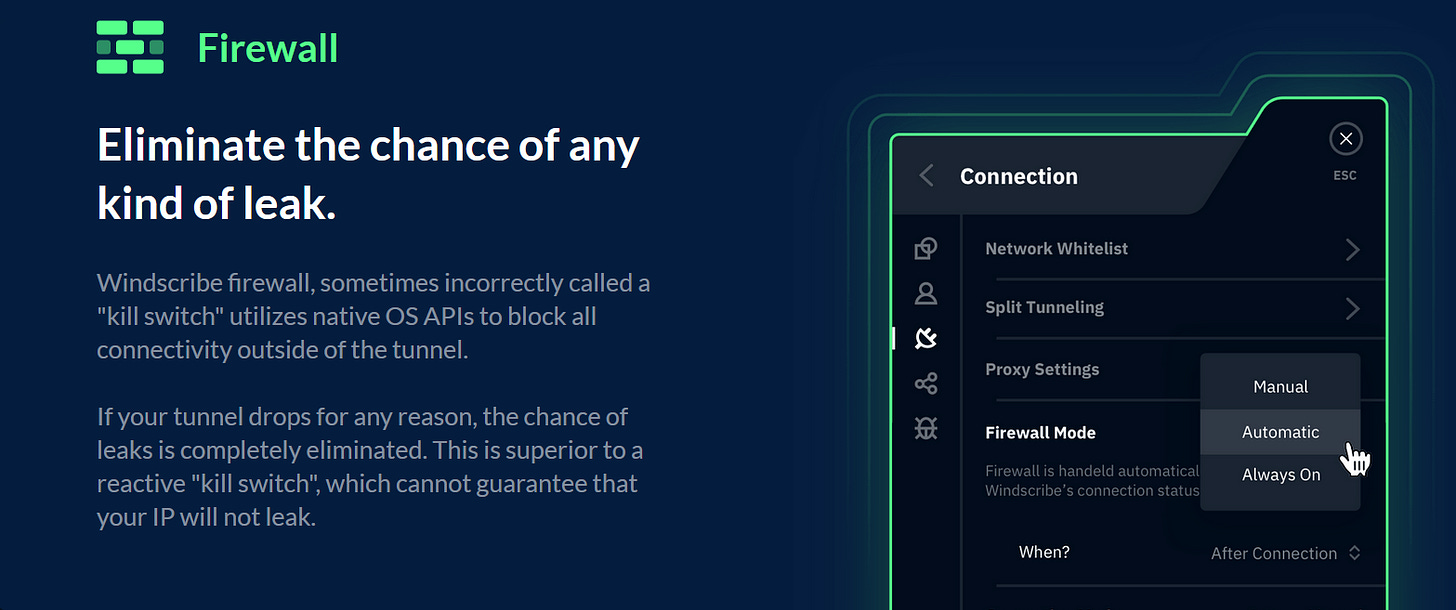
Credit: Windcribe Open Source Client: Choosing a VPN provider with an open-source client offers transparency and allows the security community to scrutinize the code for any vulnerabilities or backdoors, ensuring a more secure VPN experience.
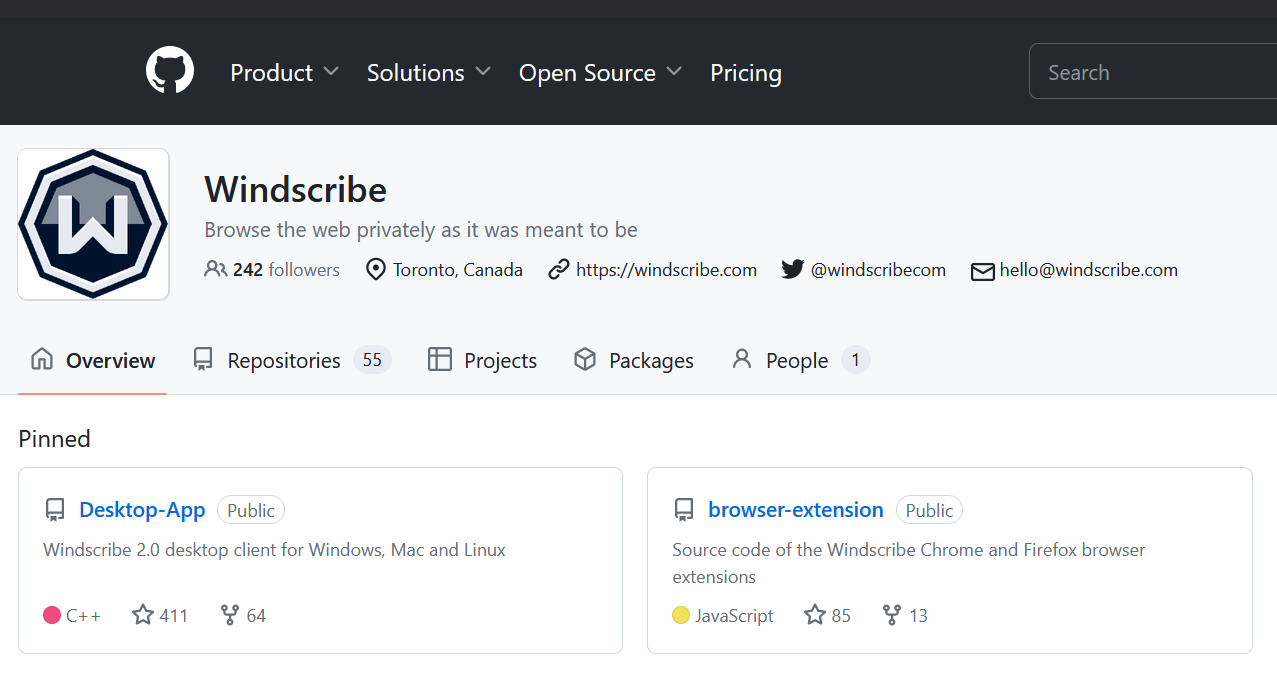
Credit: Windscribe on Github Outside 14 Eyes: The "14 Eyes" refers to a group of countries1 that cooperate in intelligence sharing. Choosing a VPN provider located outside of these jurisdictions can add an extra layer of privacy protection.

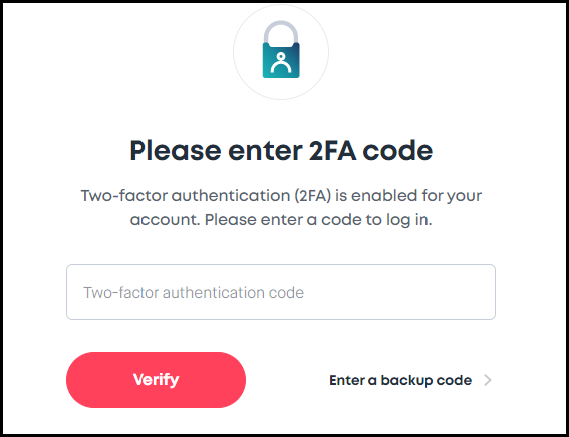
Credit: Proton VPN Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable two-factor authentication for your VPN account whenever possible. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step, usually through a mobile app or text message, when logging in.
Credit: SurfShark VPN Advanced Security Features: Some VPN providers offer additional security features like multi-hop VPN connections, which route your traffic through multiple servers for enhanced privacy, or split tunneling, which allows you to choose which traffic goes through the VPN. Consider if these features align with your security needs.
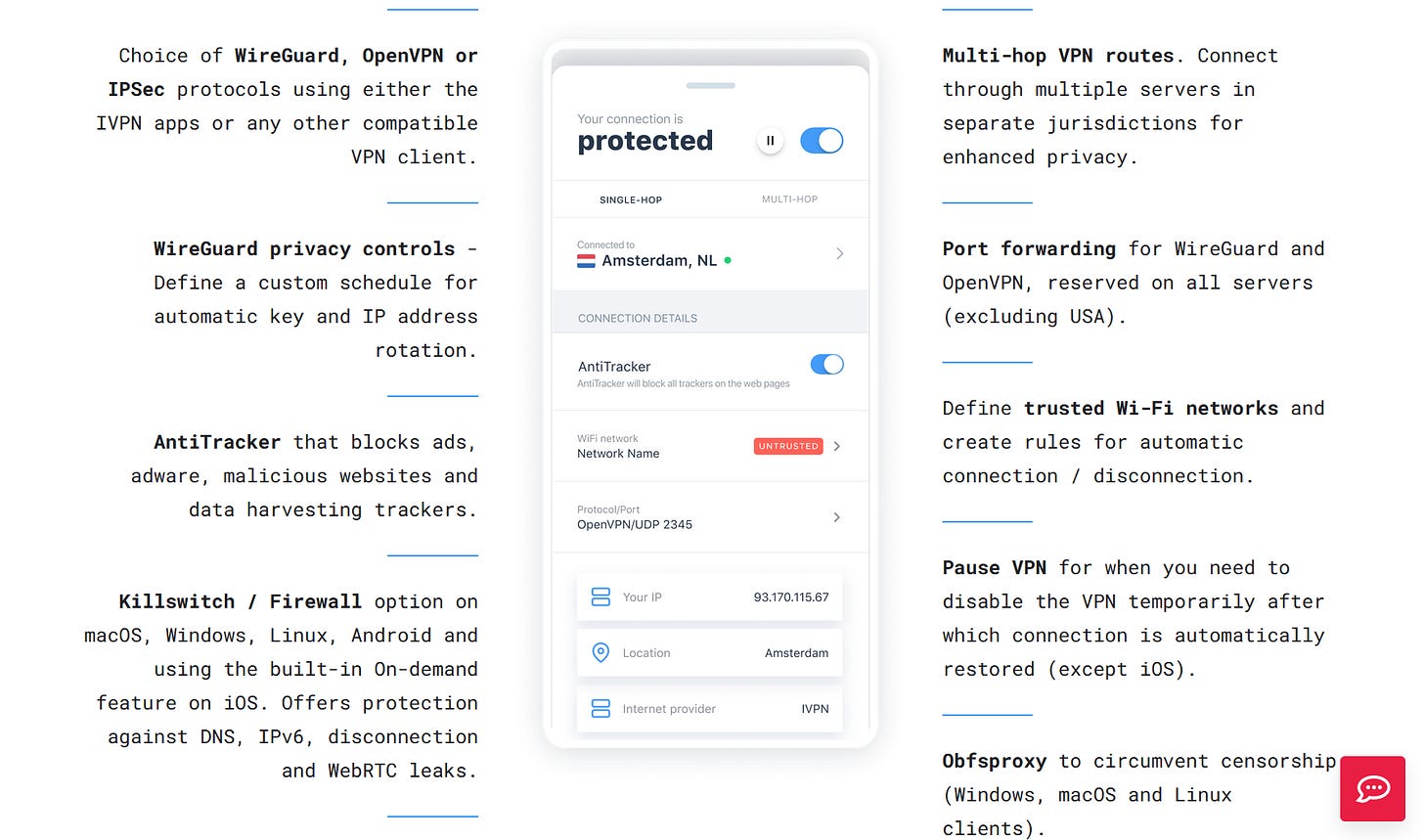
Credit: IVPN IPv6 Protection: IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol. Look for a VPN provider that offers IPv6 protection to ensure that your IPv6 traffic is also encrypted and secured.
Credit: PerfectPrivacy VPN Independent Security Audits: Look for VPN providers that have undergone independent security audits or have their services audited by reputable third-party organizations. These audits provide assurance that the VPN service operates as claimed and that there are no security vulnerabilities or privacy risks.
Full Report: Mullvad Audit Transparency: A trustworthy VPN provider will be transparent about its privacy practices, encryption protocols used, and any potential security incidents or breaches. Transparency builds confidence and helps ensure that the provider is committed to protecting your privacy and security. Look for transparency reports as well. A VPN provider that publishes regular transparency reports demonstrates a commitment to openness and accountability. These reports provide information on government data requests, DMCA takedown notices, and other relevant privacy-related issues.

Credit: OVPN Honest Marketing: Look for a VPN provider that practices honest marketing, providing accurate information about their service, features, and privacy claims. Avoid providers that make unrealistic or exaggerated promises and use false advertising.

Credit: IVPN Diskless Servers: Diskless servers are designed to run without hard drives, ensuring that no data is stored locally. This enhances security and privacy as there is no risk of data being retained or seized from physical storage devices.
Credit: Mullvad VPN Anonymous Payment Options: If you seek maximum anonymity, check if the VPN provider accepts anonymous payment methods like cryptocurrencies or cash. This can help further protect your identity and maintain privacy.

Credit: Mullvad VPN No Analytics: Ensure that the VPN provider has a strict no-analytics policy. This means they do not collect or track any information about your online activities, providing greater privacy and reducing the risk of data exposure.
Credit: NordVPN Reputation, history and User Reviews: Research the reputation of the VPN provider and read user reviews from reliable sources. Feedback from existing users can provide insights into the provider's track record in maintaining privacy and security.
Credit: Privacy Guides Clear Revenue Model: Choose a VPN provider that has a clear and transparent revenue model. It should be evident how the provider sustains its operations and funds its services. Look for providers that rely on subscription fees or other transparent sources of revenue rather than potentially compromising user data for profit.
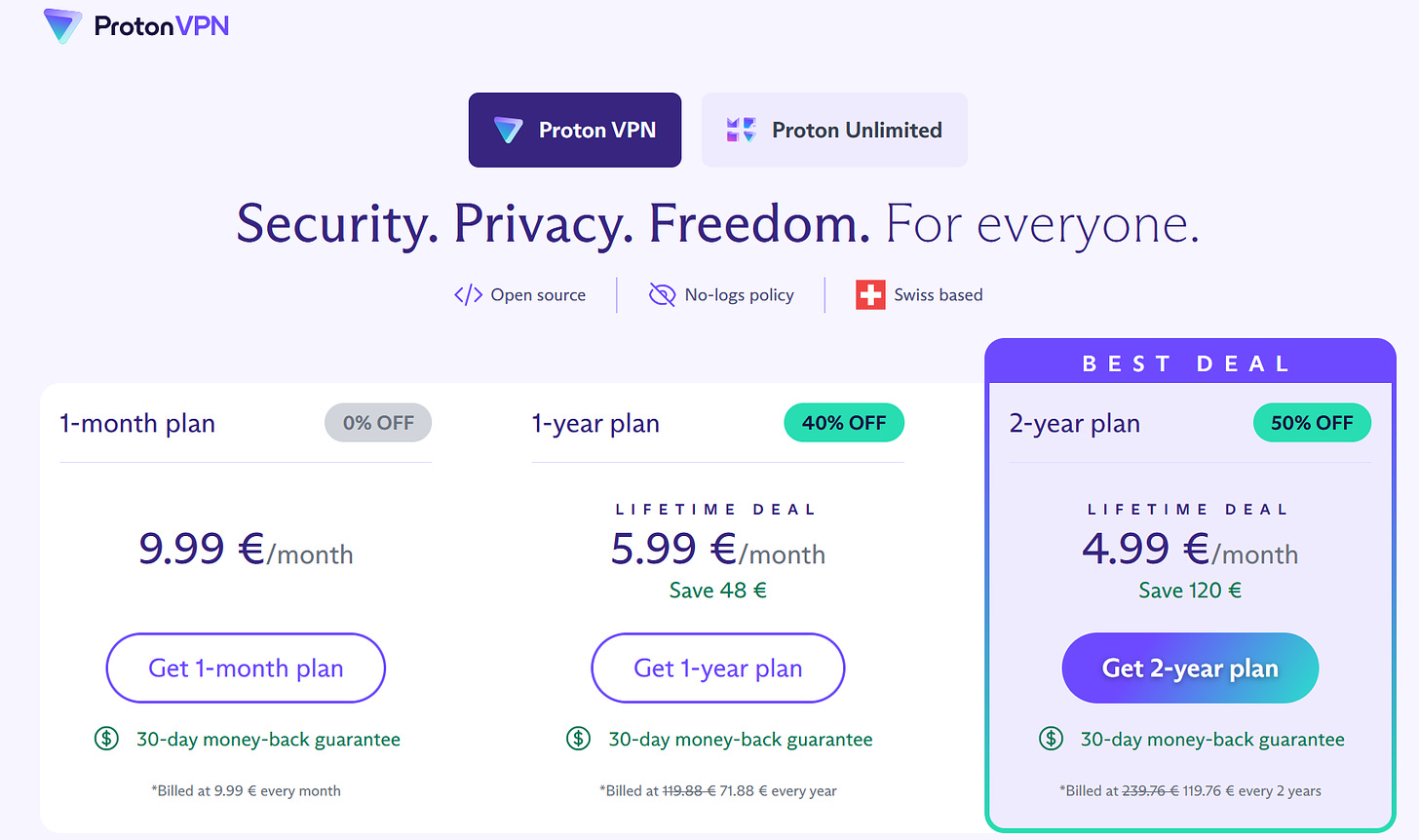
Credit: Proton VPN Supports Privacy Causes: Consider VPN providers that actively support and contribute to privacy causes, such as digital rights organizations or initiatives that promote online privacy and internet freedom. Supporting such providers can align your values with their mission.
Credit: Mullvad VPN
6) VPN Limitations: Understanding the Trade-offs and Maximizing Performance

Compatibility and device limitations: VPNs are generally compatible with most devices and operating systems, including desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. However, certain devices or platforms might have limitations or require additional setup to use a VPN effectively.
Ensure that the VPN service you choose supports the devices and platforms you intend to use. Follow the provider's instructions or documentation to set up the VPN correctly on each device.
Performance and server load: VPN performance can be affected by the number of users connected to a server. If a VPN server is overloaded with users, it may result in slower speeds and reduced performance.
Choose a VPN provider with a large number of locations, servers and a good reputation for server reliability. Consider manually selecting less crowded servers or using features like "fastest server" or "optimal location" if available.
Third-party application limitations: Certain applications or services might not work properly when using a VPN due to compatibility or security measures. For example, some banking or financial apps may block access when they detect a VPN connection.
If you encounter issues with specific applications while using a VPN, try disconnecting from the VPN temporarily for that specific activity. Alternatively, contact the VPN provider's support team for assistance or advice on resolving compatibility issues.
7) VPN Speed and Performance: Managing Realistic Expectations
When using a Virtual Private Network (VPN), it's important to keep your expectations in check and avoid soaring too high like a bird on caffeine. Sure, VPNs come with awesome perks like added security and privacy, but they can also take your internet speed on a bumpy detour. Here are some factors to consider when managing your expectations regarding VPN speed and performance:
Internet Connection Speed: The speed of your internet connection plays a significant role in determining the overall VPN performance. If you have a slow internet connection, the VPN speed will also be impacted. VPNs cannot magically increase your internet speed; they can only provide a secure connection over the existing speed.
Distance to VPN Server: The physical distance between your location and the VPN server you connect to can affect the speed. Connecting to a VPN server that is far away from your actual location may introduce latency, resulting in slower speeds. Choosing a server closer to your location can often improve performance.
Server Load: The number of users connected to a VPN server can impact its performance. If a server is overloaded with users, it may lead to reduced speeds. Choosing a less crowded server or one with better infrastructure can help improve performance.
Encryption and Protocol: VPNs use encryption to secure your data, but stronger encryption algorithms can require more processing power, potentially leading to slower speeds. Similarly, different VPN protocols have varying levels of efficiency and can affect performance. OpenVPN, for example, is generally slower compared to more lightweight protocols like WireGuard.
Device and Hardware Limitations: The performance of your device, particularly its processing power and network adapter capabilities, can influence VPN speed. Older devices or those with less powerful hardware may experience slower speeds when running a VPN.
Throttling by ISP: In some cases, Internet Service Providers (ISPs) might intentionally throttle VPN traffic to manage network congestion, enforce data caps or just to be mean to you :( This can significantly impact VPN performance, resulting in slower speeds. Using a VPN that employs obfuscation techniques or choosing servers that are less likely to be blocked can help mitigate this issue.
VPN Provider: The quality and infrastructure of the VPN provider you choose can affect speed and performance. Reputable VPN providers often invest in robust server networks and optimized configurations to ensure better performance.
8) Free VPNs: Unveiling the Hidden Costs and Risks

Repeat after me: YOU SHOULD NEVER USE A FREE VPN. A VPN service needs to have a clear and transparent way to generate revenue such as a subscription-fee or (rarely) donations. I know they may seem like a tempting treat, promising to guard your privacy and unlock restricted content without costing a penny. However, falling into the free VPN trap is like getting your hand stuck in a cookie jar of trouble, here’s why:
Data Logging and huge Privacy Concerns: Free VPN providers often need to generate revenue to sustain their operations, and they may do so by logging and selling user data. This contradicts the very purpose of using a VPN to enhance privacy. Your online activities and personal information could be collected and shared with third parties, including advertisers, which compromises your privacy. Remember: if it’s free you’re the product.
Advertisements and Malware: To generate revenue, free VPNs often display advertisements or inject them into web pages you visit. These ads can be intrusive and diminish the overall browsing experience. Moreover, some free VPNs have been found to contain malware or be involved in questionable practices, potentially putting your device and data at risk.
Trustworthiness and Transparency: The credibility of free VPN providers can be questionable. It might be hard to thoroughly research and evaluate their reputation, user reviews, and transparency about their business practices.
Security Vulnerabilities: Free VPNs may not implement robust security measures, leaving your data susceptible to leaks or breaches. They might lack features like strong encryption, secure protocols, and automatic kill switches, which are essential for maintaining a secure VPN connection.
Legal and Jurisdictional Concerns: Some free VPN providers operate in jurisdictions that may have data retention laws or be part of international surveillance alliances. This could undermine the effectiveness of using a VPN to protect your privacy since your data could still be subject to surveillance or handed over to authorities upon request.
Limited Server Options and Bandwidth: Free VPNs typically offer limited server options compared to paid services. This can result in slower speeds and restricted access to certain websites or services. Additionally, many free VPNs impose data caps or limit bandwidth usage, leading to slower and more restricted browsing experiences.
Unreliable Support and Limited Features: Free VPNs typically offer limited customer support compared to paid services. If you encounter technical issues or need assistance, you may not receive reliable support. Additionally, free VPNs often lack advanced features like split tunneling, dedicated IP addresses, or access to specialized servers.
— Congratulations, brave internet explorer, for embarking on this quest to unravel the secrets of Virtual Private Networks! Armed with the knowledge you've gained, you're now equipped to navigate the wild open web with confidence and security while using your favorite VPN!
💡Resources:
Countries in the “14 Eyes”: United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Norway, Denmark, France, Netherlands, Germany, Belgium, Italy, Sweden, Spain