Today, you’ll be learning the basics about MAC Addresses -and no, it doesn’t have anything to do with a big mac-
You’ll learn what a MAC address is in simple terms, and how to leverage it to make your devices more private and secure.
So, without any more interruptions, let’s get right into it!
What’s a MAC Address?
MAC, in the context of networking, stands for "Media Access Control." Think of a MAC address as the license plate or the ID card of your computer, or any other device connected to a network. Manufacturers are the ones that assign MAC addresses, they are generally unique to each device and can usually be found in the device's network settings. When devices connect to different Wi-Fi networks or access points, they typically broadcast their MAC addresses. This address helps routers recognize to what device they should send the data packets they receive.
MAC Addresses also help different devices to recognize each other on a network. When one device wants to send data to another device within the local network, it uses the MAC address of the target device. An example of this would be a computer sending a print request to a printer, or a phone casting a cat video to a smart TV.
MAC Address Filtering:
Since your router can see all of the MAC Addresses of devices that are connected to it, you can configure it through it’s settings interface to allow or disallow network access to certain devices. This could be used to prevent network leeches like your shady neighbor from stealing your bandwidth, or to only allow work devices to connect to a work network.
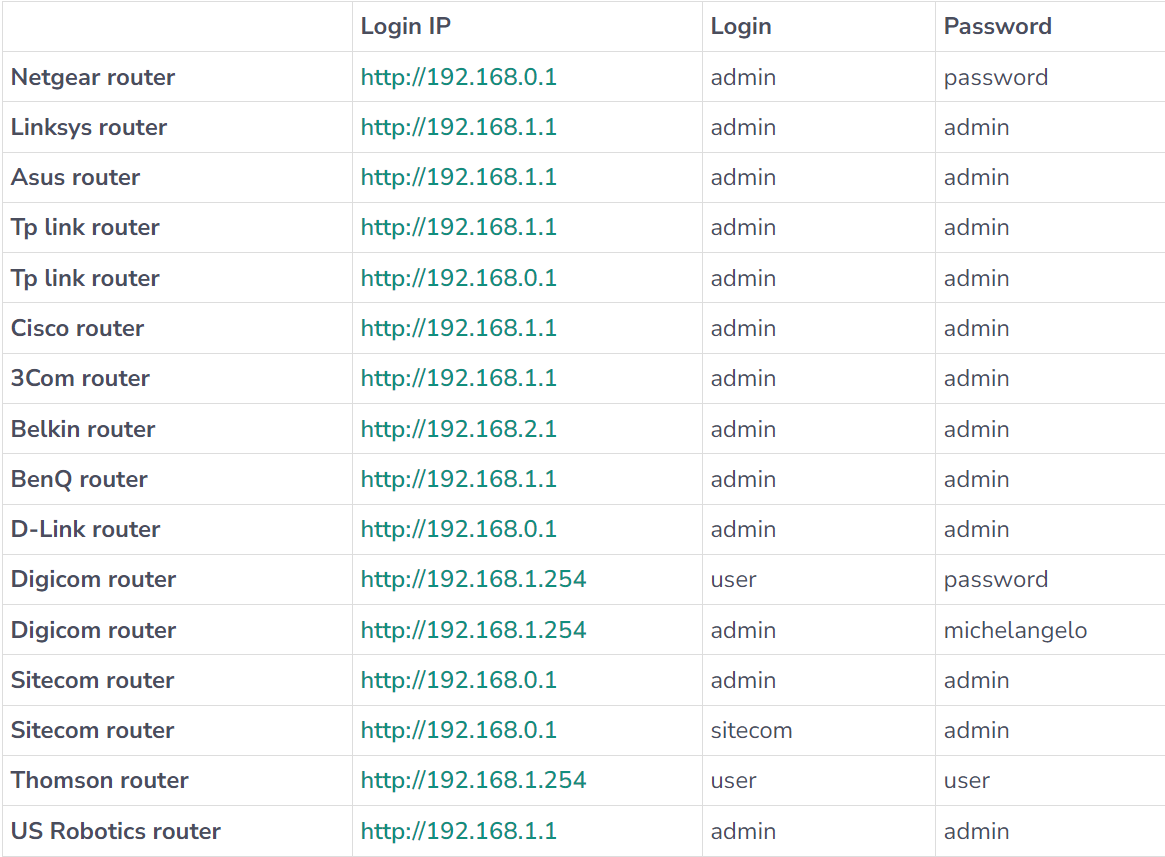
You can access the router interface by being connected to the router in question, opening a web browser and entering the router's IP address in the address bar. This IP address is often something like 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.11, then logging in to your router's administrative interface using the username and password. These credentials can be found on your router manufacturer’s website or by calling their support line if left unchanged by the user2.
Here’s a small general table of these default credentials for your convenience:
The location of MAC address filtering settings varies by router model. Look for a section named "MAC Filtering," "Wireless MAC Address Filtering," or similar.
Enable the MAC address filtering feature. Some routers allow you to choose between two modes: "Allow listed devices" or "Deny listed devices." Choose the "Allow" mode for a whitelist approach, or the “Deny” mode for a blacklist one. You'll find an option to add devices to the list. Enter the MAC addresses of the devices you want to allow or disallow and save the changes.
⚠️ Disclaimer: While MAC address filtering can add an additional layer of control to your network, it's essential to understand its limitations. This feature should not solely be relied on as a security measure because MAC addresses can be spoofed or randomized which makes the system susceptible to unauthorized access.
Protect Your Privacy By Randomizing MAC Addresses:
You can use your device’s settings to spoof and/or randomize your MAC address. Randomizing your MAC address can help you become more private by giving out a randomly generated MAC address each time you connect to a new wifi network. This makes it a little more difficult to create a profile about your device’s movements, to link your device’s activities across different locations or networks, and to potentially use your MAC address to track you for advertising or fraudulent purposes. It might potentially also help you re-connect to a wifi network if you’re being blacklisted.
Different devices offer different ways to randomize your MAC address. You can usually find it in your network settings under different names like “Random MAC/Hardware/Physical Address.”
— That’s it! Through this post you now know what a MAC address is, how to use MAC Address filtering to allow or disallow devices on your network and how to use MAC Address Randomization to become more private online. We hope you enjoyed today’s publication, ShieldUp!
Other common router addresses are:
10.0.0.1 - 10.0.1.1 - 192.168.2.1 - 192.168.11.1 - 192.168.0.1 - 192.168.0.227 - 192.168.1.254…
Users should change their default router interface’s credentials to disallow other connected devices from easily accessing it.